SAP Security is a critical component of SAP systems, designed to protect sensitive data and ensure that only authorized users have access to specific functionalities. This course will provide participants with a comprehensive understanding of SAP Security, focusing on its key features, functionalities, and best practices for implementation and management. By the end of the course, participants will be equipped with the knowledge and skills needed to secure SAP systems effectively.

Key Learning Objectives
By the end of this course, participants will be able to:
- Understand the core concepts and importance of SAP Security.
- Describe the system architecture and setup of SAP Security.
- Identify and manage access risks using risk assessment and mitigation strategies.
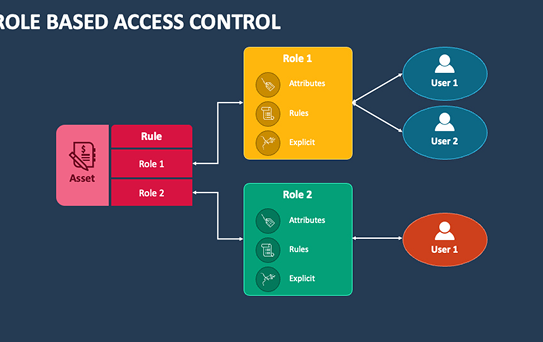
- Configure and manage user provisioning and role-based access control.
- Design and maintain effective security controls and measures.
- Implement and monitor security monitoring and reporting mechanisms.
- Customize and integrate SAP Security with other SAP solutions.
- Apply best practices and learn from real-world case studies for successful implementation.